本篇全面总结了 C++ 与 Lua 脚本交互的相关内容。内容目录:
编译并配置 Lua 库
Lua 与 C++ 交互原理
C++ 调用 Lua 脚本
Lua 调用 C++ 函数
Lua 调用 C++ 函数模块
Lua 以模块形式使用 C++ 类
Lua 以面向对象形式使用 C++ 类
Lua 与 C++ 全局数组交互
常用 API 总结
1 编译并配置 Lua 库 想要 Build 源码并直接使用 Lua 环境可以查看官网的详细步骤:lua-users wiki: Building Lua In Windows For Newbies
为了与 C++ 程序交互,这里我们使用 VS 来将 Lua 编译成动态库,供 C++ 程序调用。
首先在 VS 中新建一个 DLL 项目:
切换到 Release 模式,然后将 Lua 源码的 src 文件夹复制到工程目录下,并将其中除 lua.c 和 luac.c 之外的所有 .c 和 .h 文件添加到工程中(因为这两个文件中有 main 函数,编译时会出错,也可以把 main 改个名字)。
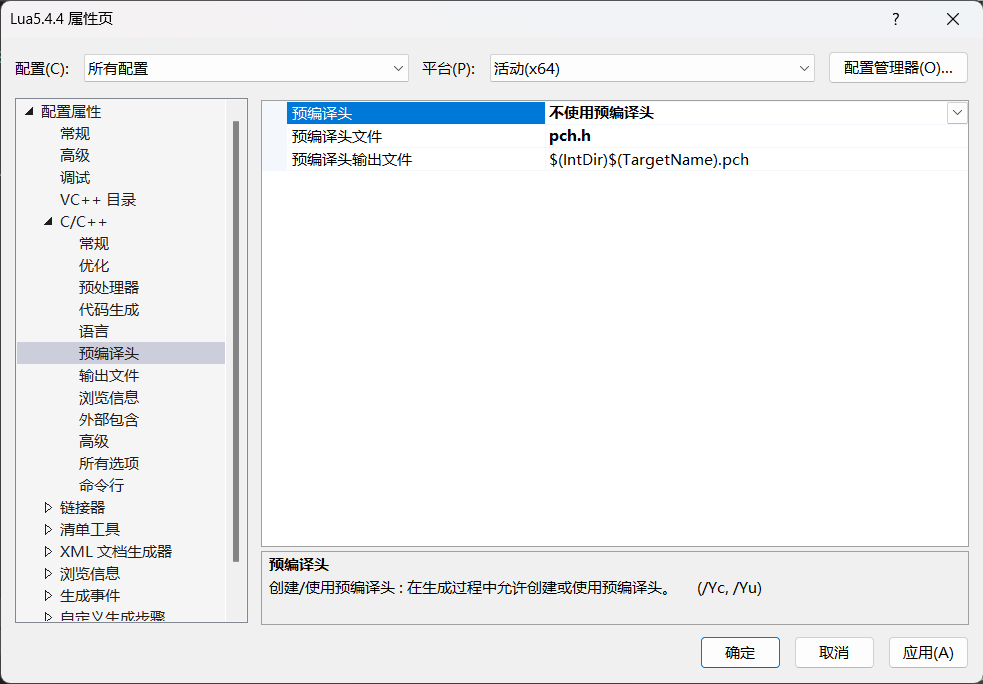
修改工程属性,C/C++ -> 预编译头 -> 不使用预编译头:
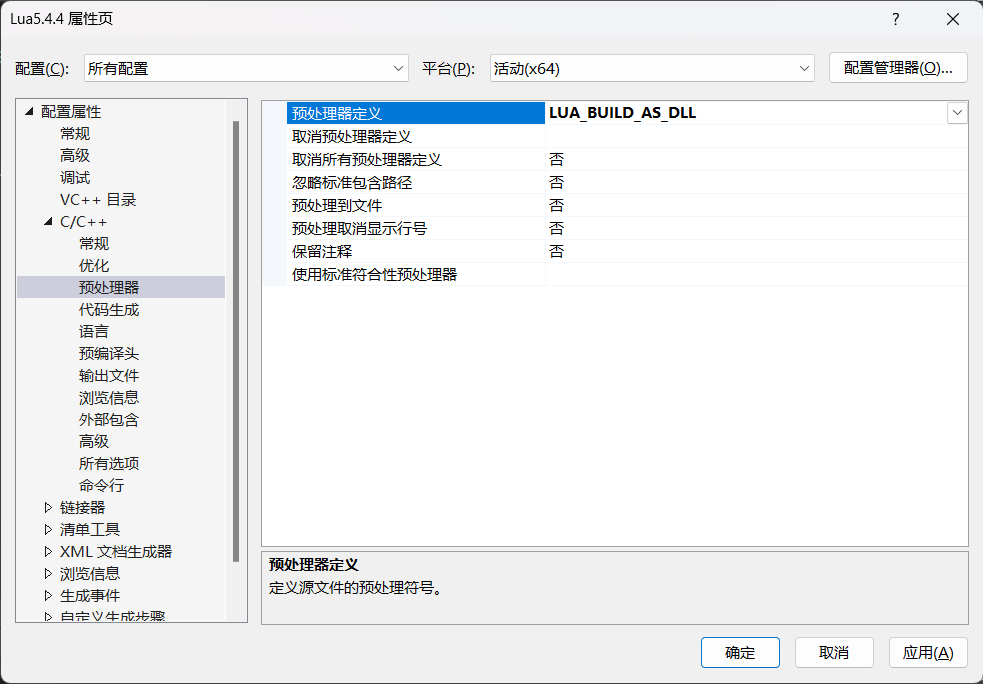
再修改:C/C++ -> 预处理器 -> 预处理器定义,加上 LUA_BUILD_AS_DLL 宏定义:
之后进行生成,就可以得到编译后的库文件了:
接下来为了方便后续使用,我们在合适的位置新建一个文件夹来放置 Lua 库和头文件:
然后将 Lua 源码中的 src 文件夹下的文件复制到 include 文件夹下,将生成的 .lib 文件复制到 lib 文件夹下。
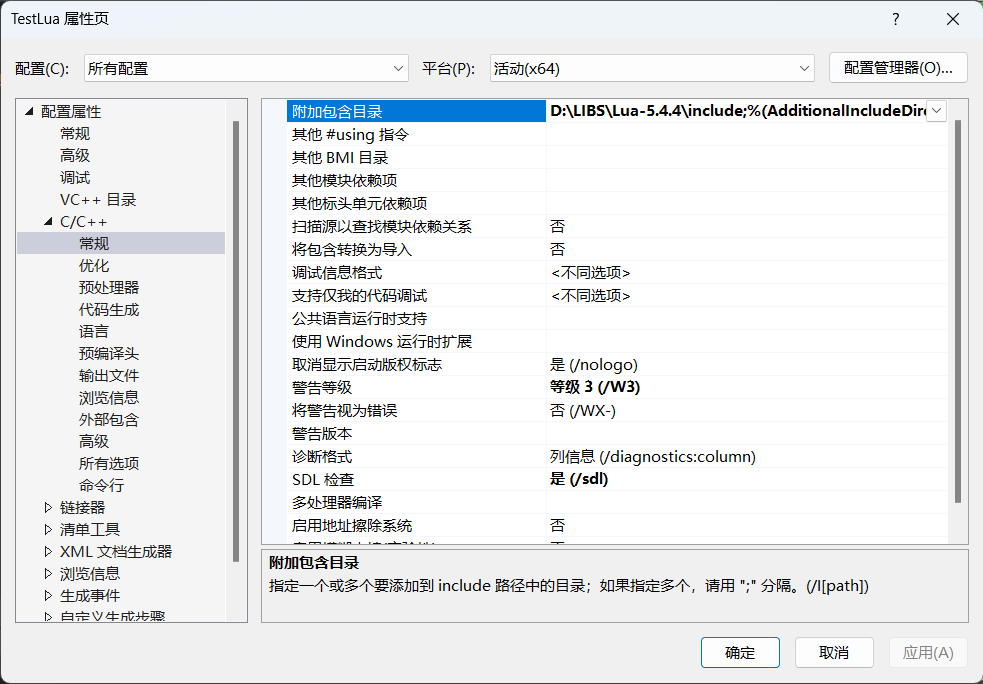
接下来新建一个 C++ 工程,然后在配置项中加入包含目录:
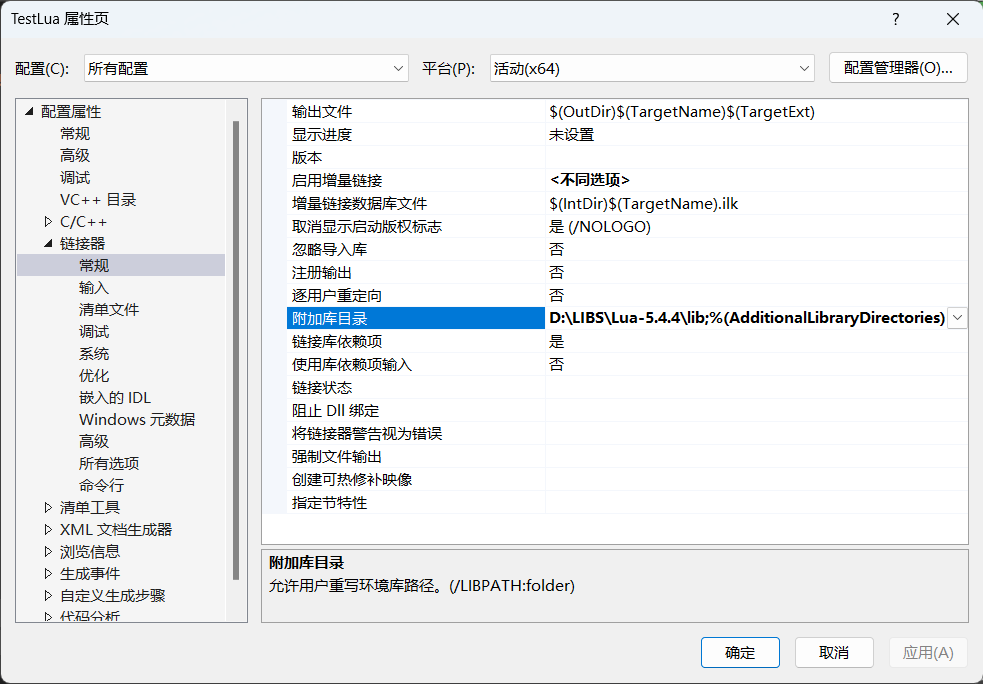
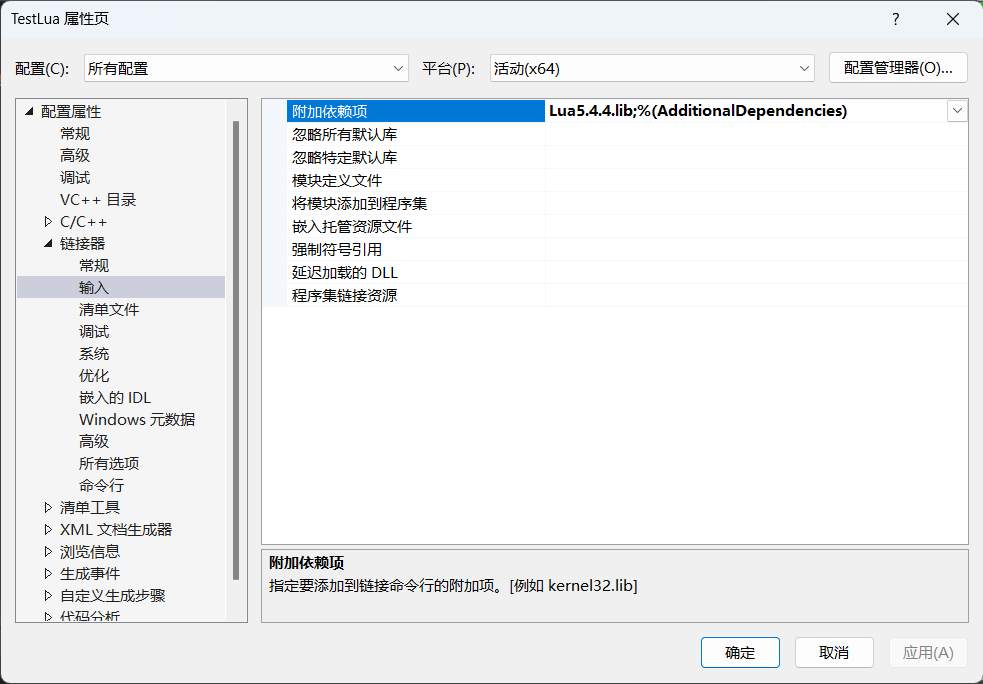
在链接器配置中添加 Lua 库目录和库文件:
之后生成项目的 Debug/Release 目录,并将 Lua 动态库 .dll 文件放到该文件夹下:
然后写一个测试程序测试是否配置成功:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 #include <iostream> #include <string.h> using namespace std; extern "C" { #include "lua.h" #include "lauxlib.h" #include "lualib.h" } void main () lua_State *L = luaL_newstate (); lua_pushstring (L, "I am so cool~" ); lua_pushnumber (L, 20 ); if (lua_isstring (L, 1 )) { cout << lua_tostring (L,1 ) << endl; } if (lua_isnumber (L, 2 )) { cout << lua_tonumber (L, 2 ) << endl; } lua_close (L); return ; }
输出:
就表明配置完成了。
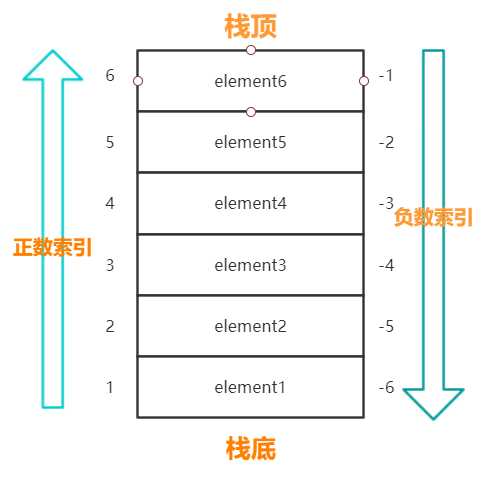
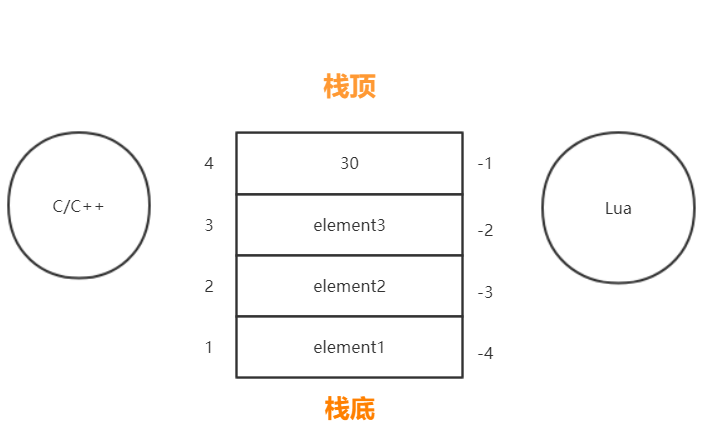
2 Lua 与 C++ 交互原理 Lua 与 C/C++ 交互是通过一个虚拟栈来实现的,这个虚拟栈实际上就是一个 struct,具体实现可以从 Lua 源码中 lstate.c 文件中的 static void stack_init (lua_State *L1, lua_State *L) 函数看起。
与常规栈不同的是 Lua 虚拟栈不仅有正向索引(正数),还有反向索引(负数),其中正数索引 1 表示栈底,负数索引 -1 表示栈顶:
于是 Lua 和 C++ 程序交互时,如果要传递值,基本原理就是:
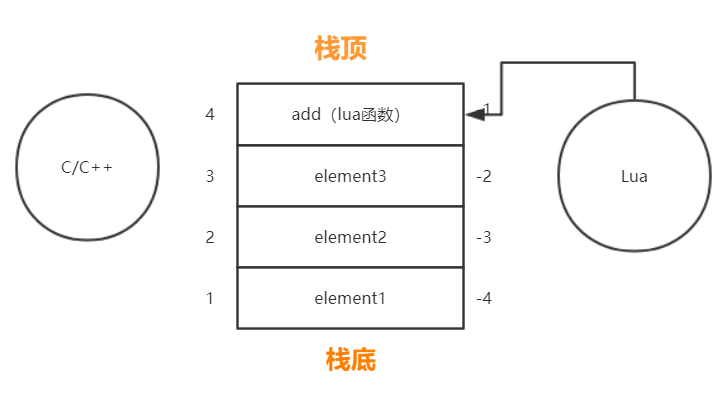
而如果要发生函数交互,过程会稍微复杂一点:
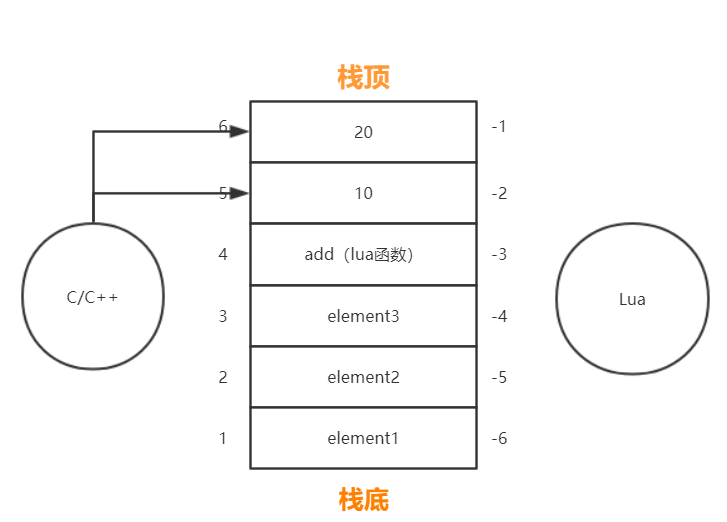
当 C++ 要调用 Lua 函数时,Lua 先将 Lua 函数压入栈中,C++ 再将数据(作为参数)继续压入栈中,然后用 API 调用栈上的 Lua 函数 + 参数,调用完后,Lua 函数和参数都会出栈,而函数计算后的值会压入栈中:
当 Lua 要调用 C++ 函数时,需要通过 API 注册符合 Lua 规范的 C++ 函数,来让 Lua 知道该 C++ 函数的定义。
存入栈中的数据可以是 Lua 中的任何数据类型,包括数值, 字符串, 指针, talbe, 闭包等等,因为 Lua 的虚拟栈在源码中是这样定义的:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 typedef union StackValue { TValue val; struct { TValuefields; unsigned short delta; } tbclist; } StackValue;
其中的数据都是用一个名为 TValue 的结构体来存储的,这个结构体中就包含了 Lua 中的所有数据类型:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 typedef union Value { struct GCObject *gc; void *p; lua_CFunction f; lua_Integer i; lua_Number n; } Value; #define TValuefields Value value_; lu_byte tt_ typedef struct TValue {TValuefields; } TValue;
更多的实现可以查看源码中的 lobject.h 文件。
Lua 和 C++ 通信时有一个符合设计原则的约定:所有的 Lua 中的值由 Lua 来管理,C/C++ 中产生的值 Lua 不知道, 类似表达了这样一种意思:”如果你(C/C++)想要什么,你告诉我(Lua),我来产生,然后放到栈上,你只能通过 api 来操作这个值,而我负责管好我的世界 “。这样的解耦很有必要,因为这可以保证只要是 Lua 中的变量,Lua 就要负责这些变量的生命周期和垃圾回收,而 C/C++ 程序就无需多虑。所以,必须由 Lua 来创建这些值。
3 C++ 调用 Lua 脚本 根据以上原理,C++ 调用 Lua 脚本时一般步骤是:
使用 luaL_newstate() 创建 Lua 状态机,返回指向虚拟栈的指针
使用 luaL_loadfile() 加载 Lua 脚本文件
使用 lua_pcall() 运行 Lua 脚本文件
需要获取 Lua 中的值时:
使用 lua_getglobal 获取值
使用 lua_toXXX 将值转化为对应的 C++ 数据类型
如果获取的值为 table 的话,可以使用 lua_getfield 和 lua_setfield 来获取和修改 table 中的元素
需要获取 Lua 中的函数时:
使用 lua_getglobal 获取函数
如果函数有参数的话,使用 lua_pushXXX 将参数依次入栈
使用 lua_pcall() 调用函数,然后从栈顶取出函数返回值即可
接下来我们创建一个简单的 Lua 脚本:
1 2 3 4 5 str = "Test Lua script." tbl = {name = "LYC" , id = 2020262914 } function add (a,b) return a + b end
然后使用 C++ 程序来调用脚本:
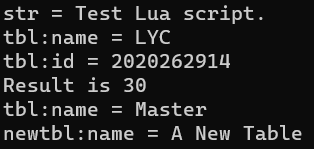
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 #include <iostream> #include <string.h> #include "lua.hpp" using namespace std;int main () lua_State* L = luaL_newstate (); if (L == NULL ) { return -1 ; } int bRet = luaL_loadfile (L, "test.lua" ); if (bRet) { cout << "load file error" << endl; return -1 ; } bRet = lua_pcall (L, 0 , 0 , 0 ); if (bRet) { cout << "pcall error" << endl; return -1 ; } lua_getglobal (L, "str" ); string str = lua_tostring (L, -1 ); cout << "str = " << str.c_str () << endl; lua_getglobal (L, "tbl" ); lua_getfield (L, -1 , "name" ); str = lua_tostring (L, -1 ); lua_getfield (L, -2 , "id" ); int id = lua_tonumber (L, -1 ); cout << "tbl:name = " << str.c_str () << endl; cout << "tbl:id = " << id << endl; lua_getglobal (L, "add" ); lua_pushnumber (L, 10 ); lua_pushnumber (L, 20 ); int iRet = lua_pcall (L, 2 , 1 , 0 ); if (iRet) { const char * pErrorMsg = lua_tostring (L, -1 ); cout << pErrorMsg << endl; lua_close (L); return -1 ; } if (lua_isnumber (L, -1 )) { int fValue = lua_tonumber (L, -1 ); cout << "Result is " << fValue << endl; } lua_pushstring (L, "Master" ); lua_setfield (L, 2 , "name" ); lua_getfield (L, 2 , "name" ); str = lua_tostring (L, -1 ); cout << "tbl:name = " << str.c_str () << endl; lua_newtable (L); lua_pushstring (L, "A New Table" ); lua_setfield (L, -2 , "name" ); lua_getfield (L, -1 , "name" ); str = lua_tostring (L, -1 ); cout << "newtbl:name = " << str.c_str () << endl; lua_close (L); return 0 ; }
输出:
当我们修改 Lua 脚本的内容:
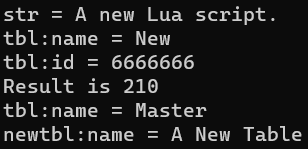
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 str = "A new Lua script." tbl = {name = "New" , id = 6666666 } function add (a, b) for i = 10 , 1 , -1 do a = a + b end return a end
重新运行的结果:
4 Lua 调用 C++ 函数 Lua 中使用 C++ 函数的一般步骤是:
将 C++ 函数包装成 Lua 环境认可的 Lua_CFunction 格式
将包装好的函数注册到 Lua 环境中
像使用普通 Lua 函数那样使用注册函数
Lua_CFunction 的基本格式如下:
1 2 3 4 static int xxxxx (lua_State *L) return 一个数字; }
函数的返回值代表函数返回结果的个数,而要获取参数则是通过将栈中某个位置的元素转换成 C++ 数据类型来实现,比如一个 3 个输入参数,2 个返回值的函数实现为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 static int average (lua_State *L) int n = lua_gettop (L); double sum = 0 ; int i; for (i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { sum += lua_tonumber (L, i); } lua_pushnumber (L, sum / n); lua_pushnumber (L, sum); return 2 ; }
然后将其注册到 Lua 环境中:
1 2 lua_register (L, "func" , average);
之后我们编写一个 Lua 脚本:
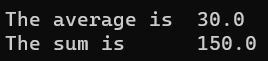
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 print ("age" , age)for k,v in pairs (newTable) do print ("k = " ,k," v = " ,v) end print ("name" , newTable.name)avg, sum = func(10 , 20 , 30 , 40 , 50 ) print ("The average is " , avg)print ("The sum is " , sum)
接下来是 C++ 部分:
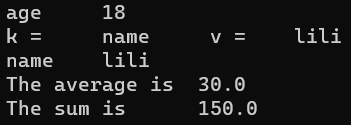
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 #include <iostream> #include <string.h> #include "lua.hpp" using namespace std;static int average (lua_State* L) int n = lua_gettop (L); double sum = 0 ; int i; for (i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { sum += lua_tonumber (L, i); } lua_pushnumber (L, sum / n); lua_pushnumber (L, sum); return 2 ; } int main () lua_State* L = luaL_newstate (); luaL_openlibs (L); lua_register (L, "func" , average); lua_pushinteger (L, 18 ); lua_setglobal (L, "age" ); lua_newtable (L); lua_pushstring (L, "lili" ); lua_setfield (L, -2 , "name" ); lua_setglobal (L, "newTable" ); luaL_dofile (L, "test.lua" ); lua_close (L); return 0 ; }
运行结果:
5 Lua 调用 C++ 函数模块 当 Lua 中需要调用多个 C++ 函数时,可以将这些函数封装成一个模块,模块实际上是一个 table,然后使用 luaL_newlib 就可以将该模块压入栈中,之后将自定义的模块注册到 Lua 环境中就可以使用了。
依然以上面的函数为例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 #include <iostream> #include <string.h> #include "lua.hpp" using namespace std;static int average (lua_State* L) int n = lua_gettop (L); double sum = 0 ; int i; for (i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { sum += lua_tonumber (L, i); } lua_pushnumber (L, sum / n); lua_pushnumber (L, sum); return 2 ; } static const luaL_Reg mylibs_funcs[] = { { "func" , average }, { NULL , NULL } }; int lua_openmylib (lua_State* L) luaL_newlib (L, mylibs_funcs); return 1 ; } static const luaL_Reg lua_reg_libs[] = { { "base" , luaopen_base }, { "mylib" , lua_openmylib }, { NULL , NULL } }; int main (int argc, char * argv[]) lua_State* L = luaL_newstate (); luaL_openlibs (L); const luaL_Reg* lua_reg = lua_reg_libs; for (; lua_reg->func; ++lua_reg) { luaL_requiref (L, lua_reg->name, lua_reg->func, 1 ); lua_pop (L, 1 ); } luaL_dofile (L, "test.lua" ); lua_close (L); return 0 ; }
在 Lua 中使用自定义模块中的函数时需要加上模块名字:
1 2 3 4 avg, sum = mylib.func(10 , 20 , 30 , 40 , 50 ) print ("The average is " , avg)print ("The sum is " , sum)
运行结果:
6 Lua 以模块形式使用 C++ 类 Lua 中还可以调用 C++ 中的类。我们可以将 C++ 中的类封装成函数模块,供 Lua 使用。
例如一个 Student 类:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 #pragma once #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;class Student { public : Student (); ~Student (); string get_name () ; void set_name (string name) unsigned int get_age () void set_age (unsigned int age) void print () private : string _name; unsigned int _age; };
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #include "Student.h" using namespace std;Student::Student () :_name("Empty" ), _age(0 ) { cout << "Student Constructor" << endl; } Student::~Student () { cout << "Student Destructor" << endl; } string Student::get_name () return _name; } void Student::set_name (string name) _name = name; } unsigned int Student::get_age () return _age; } void Student::set_age (unsigned int age) _age = age; } void Student::print () cout << "name :" << _name << " age : " << _age << endl; }
然后我们需要将这个类的各种方法以及创建这个类对象的方法注册成为 Lua 的全局函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 #pragma once #include "Student.h" #include "lua.hpp" int lua_create_new_student (lua_State* L) int lua_get_name (lua_State* L) int lua_set_name (lua_State* L) int lua_get_age (lua_State* L) int lua_set_age (lua_State* L) int lua_print (lua_State* L) static const luaL_Reg lua_reg_student_funcs[] = { { "create" , lua_create_new_student }, { "get_name" , lua_get_name }, { "set_name" , lua_set_name }, { "get_age" , lua_get_age }, { "set_age" , lua_set_age }, { "print" , lua_print }, { NULL , NULL }, }; int luaopen_student_libs (lua_State* L)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 #include "StudentRegFunc.h" int lua_create_new_student (lua_State* L) Student** s = (Student**)lua_newuserdata (L, sizeof (Student*)); *s = new Student (); return 1 ; } int lua_get_name (lua_State* L) Student** s = (Student**)lua_touserdata (L, 1 ); luaL_argcheck (L, s != NULL , 1 , "invalid user data" ); lua_settop (L, 0 ); lua_pushstring (L, (*s)->get_name ().c_str ()); return 1 ; } int lua_set_name (lua_State* L) Student** s = (Student**)lua_touserdata (L, 1 ); luaL_argcheck (L, s != NULL , 1 , "invalid user data" ); luaL_checktype (L, -1 , LUA_TSTRING); std::string name = lua_tostring (L, -1 ); (*s)->set_name (name); return 0 ; } int lua_get_age (lua_State* L) Student** s = (Student**)lua_touserdata (L, 1 ); luaL_argcheck (L, s != NULL , 1 , "invalid user data" ); lua_pushinteger (L, (*s)->get_age ()); return 1 ; } int lua_set_age (lua_State* L) Student** s = (Student**)lua_touserdata (L, 1 ); luaL_argcheck (L, s != NULL , 1 , "invalid user data" ); luaL_checktype (L, -1 , LUA_TNUMBER); (*s)->set_age ((unsigned int )lua_tointeger (L, -1 )); return 0 ; } int lua_print (lua_State* L) Student** s = (Student**)lua_touserdata (L, 1 ); luaL_argcheck (L, s != NULL , 1 , "invalid user data" ); (*s)->print (); return 0 ; } int luaopen_student_libs (lua_State* L) luaL_newlib (L, lua_reg_student_funcs); return 1 ; }
然后来编写脚本:
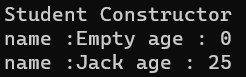
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 local student_obj = Student.create ()Student.print (student_obj) Student.set_name(student_obj,"Jack" ) Student.set_age(student_obj,25 ) Student.print (student_obj)
最后是主函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <iostream> #include <string.h> #include "Student.h" #include "StudentRegFunc.h" #include "lua.hpp" using namespace std;static const luaL_Reg lua_reg_libs[] = { { "base" , luaopen_base }, { "Student" , luaopen_student_libs}, { NULL , NULL } }; int main (int argc, char * argv[]) if (lua_State* L = luaL_newstate ()) { const luaL_Reg* lua_reg = lua_reg_libs; for (; lua_reg->func; ++lua_reg) { luaL_requiref (L, lua_reg->name, lua_reg->func, 1 ); lua_pop (L, 1 ); } if (luaL_dofile (L, "test.lua" )) { cout << lua_tostring (L, -1 ) << endl; } lua_close (L); } else { cout << "luaL_newstate error !" << endl; } return 0 ; }
运行结果:
7 Lua 以面向对象方式使用 C++ 类 上述将 C++ 类注册为函数模块的形式有一个严重的问题,那就是我们无法保证 userdata 的合法性。因为在 C++ 中,我们只是简单的判断了一下传进来的 userdata 是否为 NULL,并没有办法判断传进来的 userdata 参数是通过 Student.create 函数得到的,如果我传一个错误的 userdata 进去,程序也会继续运行,但有可能使内存遭到破坏。
一种可行的方案是,为每种类型创建一个唯一的元表。每当创建了一个 userdata 后,就用相应的元表来标记它。而每当得到一个 userdata 后,就检查它是否拥有正确的元表。由于 Lua 代码不能改变 userdata 的元表,因此也就无法传一个错误的 userdata 进去。
为每个 userdata 都创建一个元表,那就需要有个地方来存储这个新的元表。在 Lua 中,通常习惯是将所有新的 C++ 类型注册到注册表中,以一个类型名作为 key,元表作为 value。由于注册表中还有其它的内容,所以必须小心地选择类型名,以避免与 key 冲突。
具体的实现可以查看:Lua和C++交互:在Lua中以面向对象的方式使用C++注册的类
8 Lua 与 C++ 全局数组交互 具体查看:Lua和C++交互:全局数组交互
9 常用 API 总结 9.1 虚拟栈基本操作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 int lua_gettop (lua_State *L) void lua_settop (lua_State *L, int idx) void lua_pushvalue (lua_State *L, int idx) void lua_remove (lua_State *L, int idx) void lua_insert (lua_State *L, int idx) void lua_replace (lua_State *L, int idx) int lua_checkstack (lua_State *L, int n)
9.2 数据压栈 lua_pushXXX:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 LUA_API void (lua_pushnil) (lua_State *L) ;LUA_API void (lua_pushnumber) (lua_State *L, lua_Number n) ;LUA_API void (lua_pushinteger) (lua_State *L, lua_Integer n) ;LUA_API const char *(lua_pushlstring) (lua_State *L, const char *s, size_t len); LUA_API const char *(lua_pushstring) (lua_State *L, const char *s); LUA_API const char *(lua_pushvfstring) (lua_State *L, const char *fmt, va_list argp); LUA_API const char *(lua_pushfstring) (lua_State *L, const char *fmt, ...); LUA_API void (lua_pushcclosure) (lua_State *L, lua_CFunction fn, int n) ;LUA_API void (lua_pushboolean) (lua_State *L, int b) ;LUA_API void (lua_pushlightuserdata) (lua_State *L, void *p) ;LUA_API int (lua_pushthread) (lua_State *L) ;
9.3 判断栈中数据类型 lua_isXXX:
1 2 3 4 5 6 LUA_API int (lua_isnumber) (lua_State *L, int idx) ;LUA_API int (lua_isstring) (lua_State *L, int idx) ;LUA_API int (lua_iscfunction) (lua_State *L, int idx) ;LUA_API int (lua_isinteger) (lua_State *L, int idx) ;LUA_API int (lua_isuserdata) (lua_State *L, int idx) ;LUA_API int (lua_type) (lua_State *L, int idx) ;
9.4 获取栈中数据 lua_toXXX:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 LUA_API lua_Number (lua_tonumberx) (lua_State *L, int idx, int *isnum) ;LUA_API lua_Integer (lua_tointegerx) (lua_State *L, int idx, int *isnum) ;LUA_API int (lua_toboolean) (lua_State *L, int idx) ;LUA_API const char *(lua_tolstring) (lua_State *L, int idx, size_t *len); LUA_API size_t (lua_rawlen) (lua_State *L, int idx) ;LUA_API lua_CFunction (lua_tocfunction) (lua_State *L, int idx) ;LUA_API void *(lua_touserdata) (lua_State *L, int idx); LUA_API lua_State *(lua_tothread) (lua_State *L, int idx); LUA_API const void *(lua_topointer) (lua_State *L, int idx);
9.5 获取栈中数据 lua_getXXX:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 LUA_API int (lua_getglobal) (lua_State *L, const char *name) ;LUA_API int (lua_gettable) (lua_State *L, int idx) ;LUA_API int (lua_getfield) (lua_State *L, int idx, const char *k) ;LUA_API int (lua_geti) (lua_State *L, int idx, lua_Integer n) ;LUA_API int (lua_rawget) (lua_State *L, int idx) ;LUA_API int (lua_rawgeti) (lua_State *L, int idx, lua_Integer n) ;LUA_API int (lua_rawgetp) (lua_State *L, int idx, const void *p) ; LUA_API void (lua_createtable) (lua_State *L, int narr, int nrec) ;LUA_API void *(lua_newuserdata) (lua_State *L, size_t sz); LUA_API int (lua_getmetatable) (lua_State *L, int objindex) ;LUA_API int (lua_getuservalue) (lua_State *L, int idx) ;
9.6 向栈中写入数据 lua_setXXX:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 LUA_API void (lua_setglobal) (lua_State *L, const char *name) ;LUA_API void (lua_settable) (lua_State *L, int idx) ;LUA_API void (lua_setfield) (lua_State *L, int idx, const char *k) ;LUA_API void (lua_seti) (lua_State *L, int idx, lua_Integer n) ;LUA_API void (lua_rawset) (lua_State *L, int idx) ;LUA_API void (lua_rawseti) (lua_State *L, int idx, lua_Integer n) ;LUA_API void (lua_rawsetp) (lua_State *L, int idx, const void *p) ;LUA_API int (lua_setmetatable) (lua_State *L, int objindex) ;LUA_API void (lua_setuservalue) (lua_State *L, int idx) ;
10 参考资料